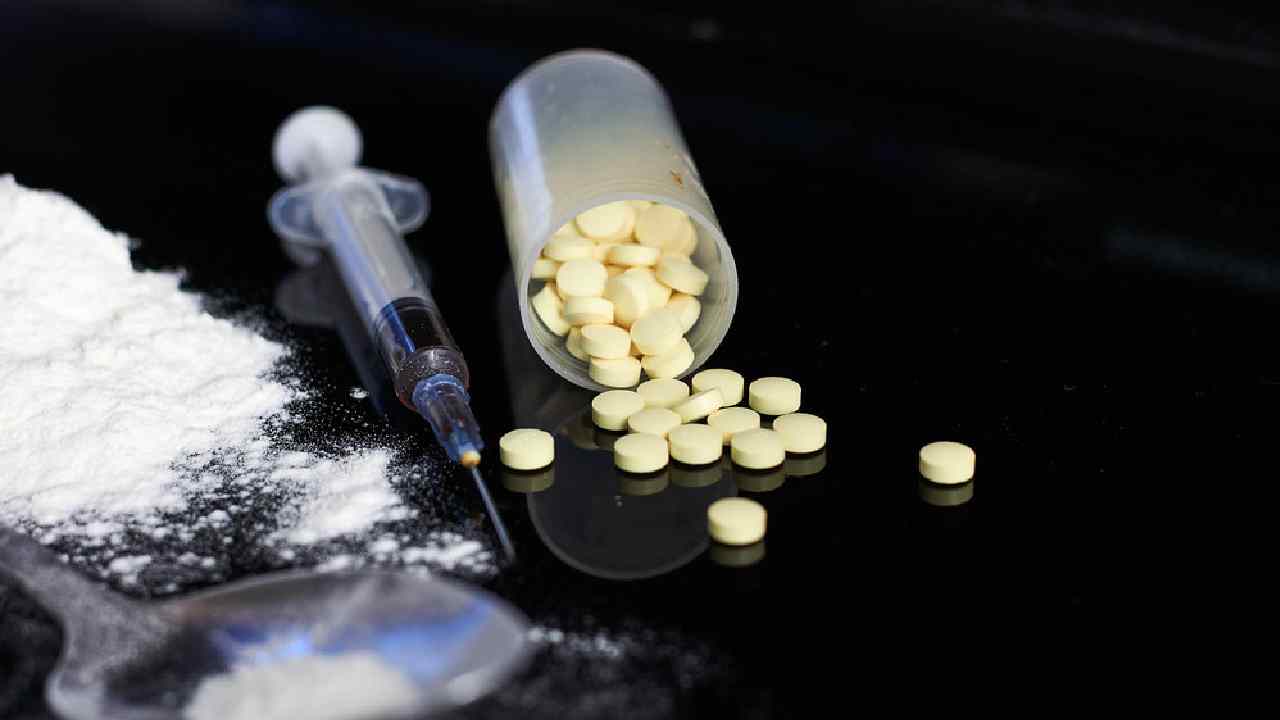
The UN Office on Drugs and Crime’s (UNODC) “World Drug Report 2022” said that cannabis legalisation in parts of the world appears to have accelerated its use and other drugs. The report also flagged various related health impact due to increased consumption. The report released on June 27 also details the record rise in the manufacturing of cocaine, the expansion of synthetic drugs to new markets, and continued gaps in the availability of drug treatments, especially for women.
According to UNODC, around 284 million people between the age of 15 to 64 used drugs worldwide in 2020— a 26% over the previous decade. Young people are using more drugs, with use levels today in many countries higher than with the previous generation. In Africa and Latin America, people under 35 represent the majority of people being treated for drug use disorders.
Globally, the report estimates, that 11.2 million people were injecting drugs. Around half of them were living with Hepatitis C, 1.4 million were living with HIV, and 1.2 million were living with both. Reacting to these findings, UNODC Executive Director Ghada Waly stated: “Numbers for the manufacturing and seizures of many illicit drugs are hitting record highs, even as global emergencies are deepening vulnerabilities.
At the same time, misperceptions regarding the magnitude of the problem and the associated harms are depriving people of care and treatment and driving young people towards harmful behaviour. We need to devote the necessary resources and attention to addressing every aspect of the world drug problem, including the provision of evidence-based care to all who need it, and we need to improve the knowledge base on how illicit drugs relate to other urgent challenges, such as conflicts and environmental degradation.”
The report further emphasises the importance of galvanising the international community, governments, civil society, and all stakeholders to take urgent action to protect people, including by strengthening drug use prevention and treatment and by tackling illicit drug supply. The report says that cannabis legalisation in North America appears to have increased daily cannabis use, especially potent cannabis products, and particularly among young adults. Associated increases in people with psychiatric disorders, suicides and hospitalisations have also been reported. However, legalisation has also increased tax revenues and generally reduced arrest rates for cannabis possession.
Cocaine manufacturing was at a record high in 2020, registering a growth of 11% from 2019 to 1,982 ton. Cocaine seizures also increased, despite the Covid-19 pandemic, to a record 1,424 ton in 2020. Nearly 90% of cocaine seized globally in 2021 was trafficked in containers by sea. Seizure data suggest that cocaine trafficking is expanding to other regions outside the main markets of North America and Europe, with increased levels of trafficking to Africa and Asia.
Trafficking of methamphetamine continues to expand geographically, with 117 countries reporting seizures of methamphetamine in 2016‒20 versus 84 in 2006‒2010. Meanwhile, the quantities of methamphetamine seized grew five-fold between 2010 and 2020. Record high seizures of methamphetamine were reported from South-West Asia, increasing by 50% in 2020 from 2019.
Opium production worldwide grew by seven percent between 2020 and 2021 to 7,930 ton—predominantly due to an increase in production in Afghanistan. However, the global area under opium poppy cultivation fell by 16% to 246,800 hectares during the same period. In the United States and Canada, overdose deaths, predominantly driven by an epidemic of the non-medical use of fentanyl, continue to break records. Preliminary estimates in the United States point to more than 107,000 drug overdose deaths in 2021, up from nearly 92,000 in 2020.
Great inequality remains in the availability of pharmaceutical opioids for medical consumption. In 2020, there were 7,500 more doses per 1 million inhabitants of controlled pain medication in North America than in West and Central Africa, states the report.
This year’s report also highlights that illicit drug economies can flourish in situations of conflict and where the rule of law is weak, and in turn can prolong or fuel conflict. Information from the Middle East and South-East Asia suggest that conflict situations can act as a magnet for the manufacture of synthetic drugs, which can be produced anywhere. This effect may be greater when the conflict area is close to large consumer markets.
Historically, parties to conflict have used drugs to finance conflict and generate income. The 2022 World Drug Report also reveals that conflicts may also disrupt and shift drug trafficking routes, as has happened in the Balkans and more recently in Ukraine. There was a significant increase in the number of reported clandestine laboratories in Ukraine, skyrocketing from 17 dismantled laboratories in 2019 to 79 in 2020. Sixty-seven out of these laboratories were producing amphetamines, up from five in 2019—the highest number of dismantled laboratories reported in any given country in 2020.
Illicit drug markets, according to the report, can have local, community, or individual-level impacts on the environment. Key findings include that the carbon footprint of indoor cannabis cultivation is between 16 to 100 times more than outdoor cannabis cultivation on average and that the footprint of one kilogram of cocaine is 30 times greater than that of cocoa beans.
Other environmental impacts include substantial deforestation associated with illicit cocoa cultivation, waste generated during synthetic drug manufacture that can be 5 to 30 times the volume of the end product, and the dumping of waste which can affecting soil, water and air directly, as well as organisms, animals and the food chain indirectly.
Globally, women remain are in the minority when it comes to drug usage, yet they tend to increase their rate of drug consumption and progress to drug use disorders at a much faster rate than men do. Women now represent an estimated 45 to 49% of end users of amphetamines and non-medical users of pharmaceutical stimulants, pharmaceutical opioids, sedatives, and tranquillizers.
The treatment gap remains large for women globally. Although women represent almost one in two amphetamines users, they constitute only one in five people in treatment for amphetamine use disorders. The World Drug Report 2022 also spotlights the wide range of roles fulfilled by women in the global cocaine economy, including cultivating coca, transporting small quantities of drugs, selling to consumers, and smuggling into prisons.