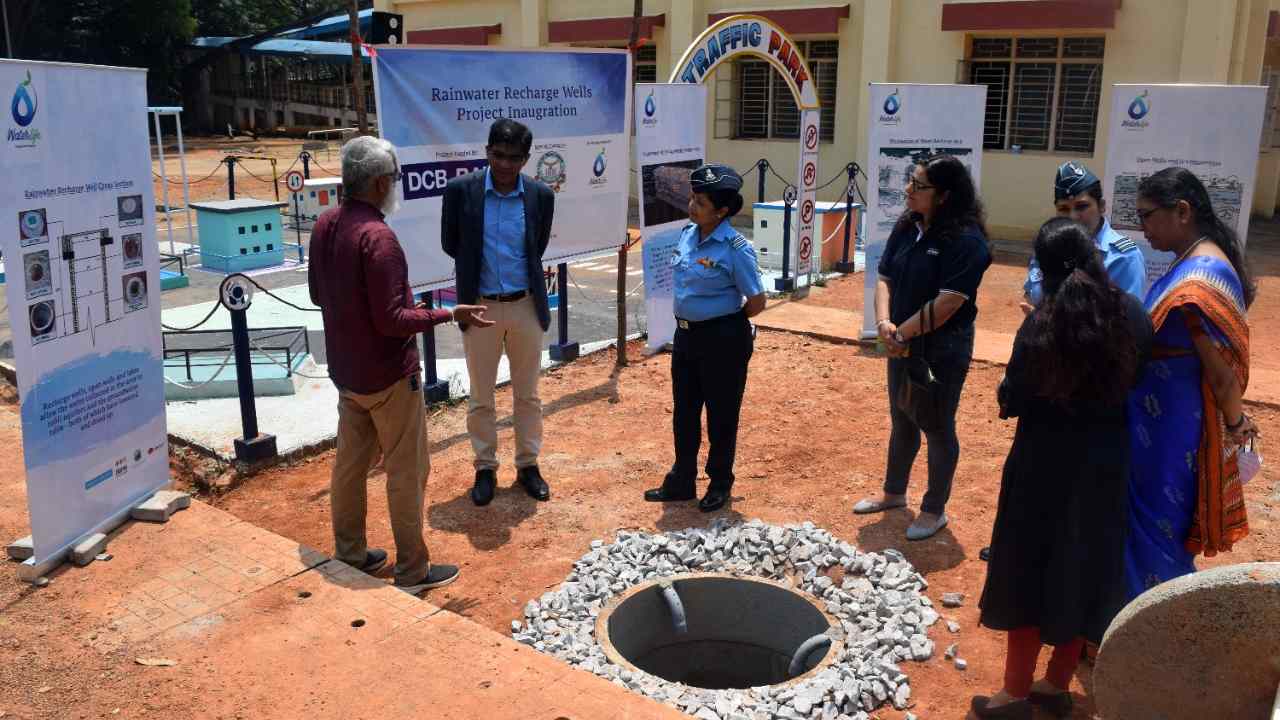
In an effort to recharge groundwater, DCB Bank in association with India Care Foundation launched a sustainable project of 25 rainwater recharge wells at Jalahalli, a suburb of Bangalore. The pilot project will eventually expand to other parts of Bangalore.
The project also aims to provide livelihood opportunities to the community of Manu Vaddar (Traditional Well Diggers).
Gaurav Mehta, the bank’s head of marketing and corporate social responsibility said, “The rainwater recharge well is a very powerful tool to manage groundwater for a city–especially Bengaluru. They also help in urban flood control, counters reduced recharge due to urbanisation and help monitor the revival of the shallow unconfined aquifer, which historically was Bengaluru’s source of domestic water. If ever there was a simple, powerful image or symbol that can both communicate and achieve physical outcomes for a city’s rainwater and groundwater management, it is the recharge well.”
RRW (Rainwater Recharge Wells) is a powerful groundwater management tool that helps protect and restore aquatic ecosystems such as rivers, lakes, wetlands and wetlands. In Bangalore, RRWs will help control urban flash floods while replenishing the recharge of a dwindling aquatic ecosystem by developing, monitoring and reactivating unregulated shallow reservoirs that traditionally supply domestic water to the city. This will help transfer excess salt accumulated in the core zone to deeper soil or groundwater systems, help plant roots increase groundwater saturation, and reduce stormwater runoff.
As the RRWs are dug manually, the initiative aims to provide livelihood opportunities to the traditional bank well-digger community who struggle to find regular employment to the best of their ability. Each RRW will require at least 3-4 people to build and operate, providing well diggers with enough income to support their families for a month under this initiative.