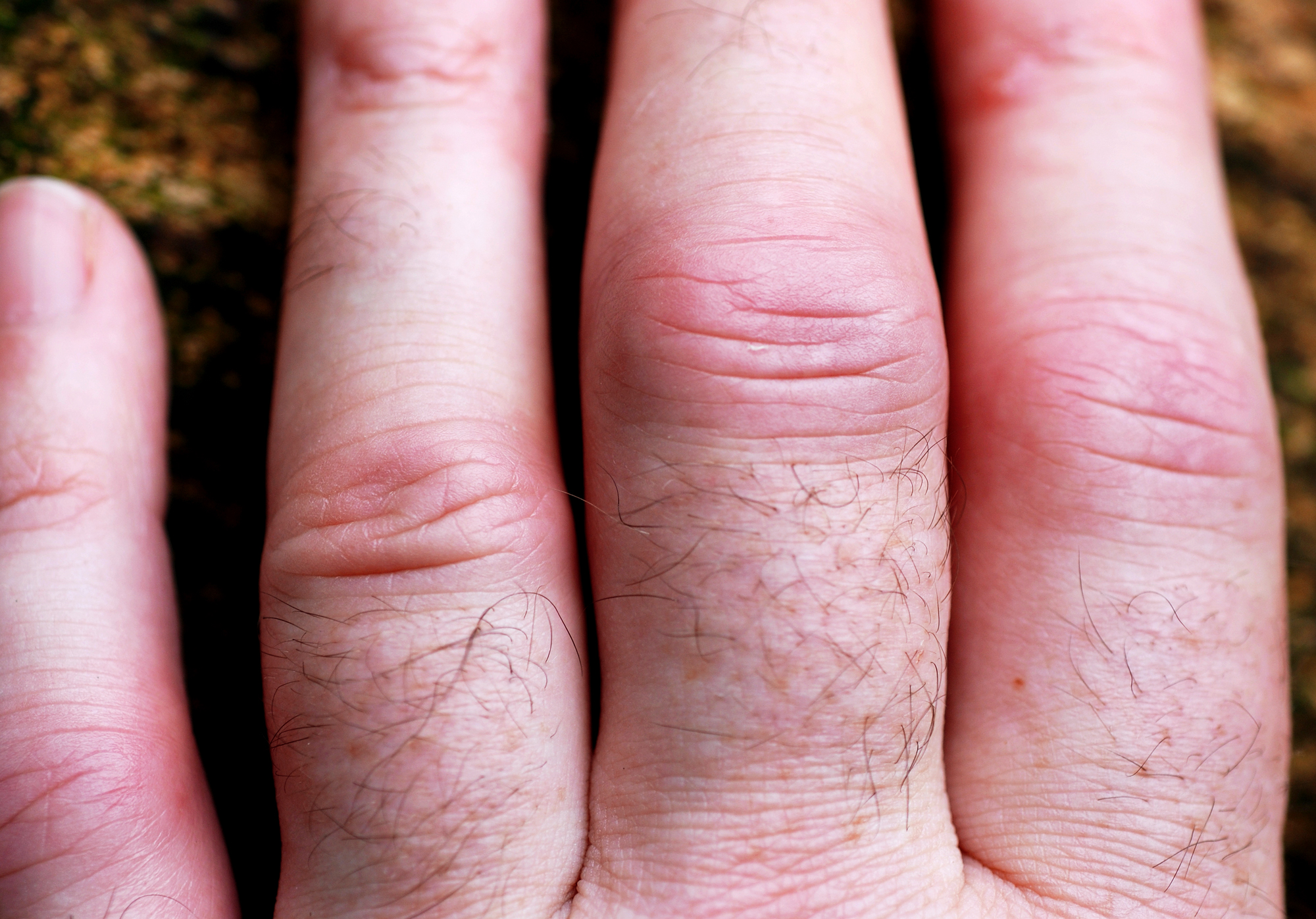
A newly synthesized biocompatible therapeutic nano-micelle drug delivery system combined with anti-inflammatory drugs has shown improved potential to cure rheumatoid arthritis at the lab level. It can help ameliorate the pain associated with the disease as well as cure the disease by restoring cartilage integrity which provides the flexibility to the bone.
Inflammation plays an important role in the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). As a result, strategies for treating RA have been largely focused on providing symptomatic relief from pain and permanent cure is not available to date. Methotrexate (MTX) is considered as golden standard for the therapy of the disease but due to its severe side effects, researchers are currently looking for alternate drugs or strategies to overcome the disease.
Scientists from Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Mohali, an autonomous institute of Department of Science and Technology, explored the potential of the anti-inflammatory FDA-approved drug 9-aminoacridine (9AA) and the natural compound caffeic acid (CA), generally found in coffee or wine (reported to possess significant anti-arthritic potential) conjugated to nano micelles, an amphiphilic molecule that forms spherical structure when immersed in water, for the treatment of RA.
A research group led by Dr. Rehan Khan, Scientist, along with Senior Research Fellow Mr. Akshay Vyawahare, has developed a therapeutic nano-micelle loaded with an anti-inflammatory drug (9AA). When administered, this shows site-specific inhibition of inflammatory mediators due to activation of NR4A1 gene (Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 4 Group A Member 1), which regulates inflammatory mechanism by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines by Fluorescent 9 aminoacridine (FDA-approved drug molecule). The nano micelle itself has potential to provide therapeutic effect, but when combined with anti-inflammatory drug, it showed enhanced potential to cure rheumatoid arthritis experimentally by inhibiting joint damage and cartilage degradation. The new strategy inhibits joint damage and cartilage degradation and showed short-term (21 days) disease eradication and long-term (45 days) protection from the reappearance of the disease.
This drug delivery system is simple, cost-effective, safe, and has significant translational potential. The nano-formulation so far tested on rats and published in ACS Nano may bring long-term relief for numerous RA patients in the future by suppressing the disease severity of Rheumatoid arthritis.