Bhulah Valley in Mandi is where Himachal Pradesh’s first biodiversity park has been set up at a cost of ₹1 crore and would host both researchers and tourists.
Set up under the National Mission on Himalayan Studies (NMHS) by the state forest department, the park has been designed to link tourism activities with providing new opportunities for researchers to conduct in-depth exploration of various medicinal herbs found in the Himalayas that are on the verge of extinction, say news reports.
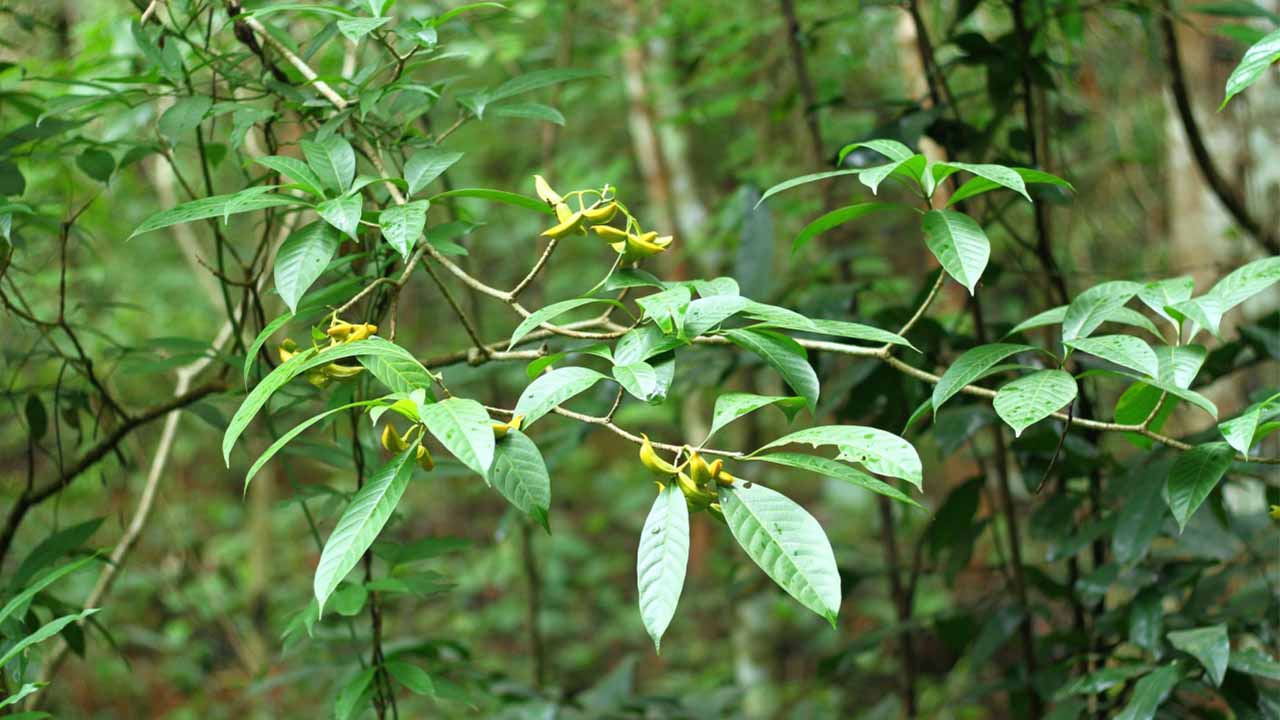
The biodiversity park has a herbal nursery to conserve herbs that are about to go extinct in the mountains. The park has Trillidium Govanianum (Nagchhatri), Dhoop, Picrorhiza Kurroa, Sarpagandha, Swertia Chirayita, Barbari plant and many similar herbs and shrubs on display. Built on five hectares, this fenced park has facilities for researchers. Any research scholar can avail information about 1,200 plants of different species available here.
The biodiversity park has amphitheatres, two log huts, a water harvesting structure, an internal tank, a 5KW power generation project, bird nests, and a sales centre. Two tree huts have also been built for tourists to enjoy the views of the park. The other attractions include nature trails of about 2 km and a 25 ft high and 160-metre-long tree walk along with seven footbridges.
Himachal Pradesh is bestowed with distinctive floral and faunal biodiversity having aesthetic, Cultural, commercial and genetic values. It is a mountainous state and has a vast repository of flora and fauna having profuse variation in intra and inter-species levels. Variable treasures of the biological resources are because of their varied topography, geological formation, altitudinal ranges and climatic conditions. The range of biodiversity elements represented in the State varies from the sub-tropical region to that of the temperate, dry temperate and alpine region. 95 percent of the floral and faunal species available in the State are endemic and 5 percent of the other species existing are of exotic nature.
What is a Biodiversity?
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety, variability and processes, within and between all micro-organisms, plants and animals both wild and domesticated and the ecological systems which they co-exist and inhabit. It starts with genes and manifests itself as organisms, species, populations and communities which lead to the formation of the ecosystem, landscape and ultimately biosphere. Biodiversity manifests at three levels:
- Genetic Diversity: diversity of genes within a species. There is genetic variability among the populations and individuals of the same species.
- Species Diversity: diversity among species in an ecosystem.
- Ecosystem diversity: diversity at a higher level of organization, the ecosystem level