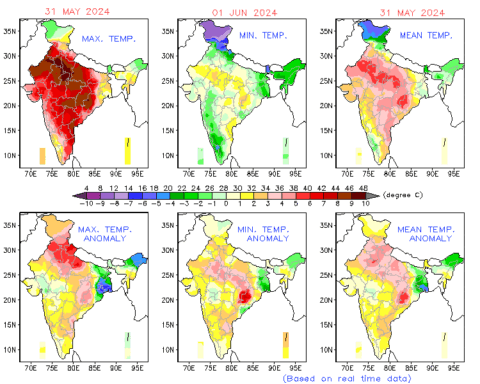
As a result of eating food contaminated with bacteria, viruses, parasites or chemicals, 600 million people fall ill every year, that is, almost every 10th inhabitant of the planet. 420,000 of them die as a result of foodborne illness, said World Health Organization (WHO)
Generally, foodborne illnesses are infectious diseases or intoxications caused by bacteria, viruses, or chemicals that enter the body through contaminated water or food. They cause over 200 diseases from diarrhoea to cancer. Foodborne pathogens can cause severe diarrhoea or disabling infectious diseases, including meningitis.
Contamination of food with chemicals can lead to acute poisoning or the development of chronic diseases such as cancer. Foodborne illness can cause long-term disability and death. Types of unsafe food include raw animal foods, fruits and vegetables contaminated with faeces, and raw shellfish containing marine biotoxins.
Urbanization and changing consumer behaviour, including the spread of tourism, are leading to an increase in the number of people buying and eating food prepared in public places. In the context of globalization, the demand for an ever wider range of food products is growing, which leads to the complexity and lengthening of the global food chain.
Growth in the global population and demand for food is intensifying and industrializing the crop and livestock sectors, creating both new opportunities and new threats to food security. Climate change is also predicted to have a negative impact on food safety.
All of these issues place additional responsibility on food producers and food workers to ensure food safety. With increasing speeds and distances for the movement of food products, local incidents can rapidly escalate into international emergencies.